Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compare to Cowan & Agol (2011)#
This example compares our thermal inertia model to that of Cowan and Agol [2011].
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from astropy import units as u
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import VSPEC.gcm.heat_transfer as ht
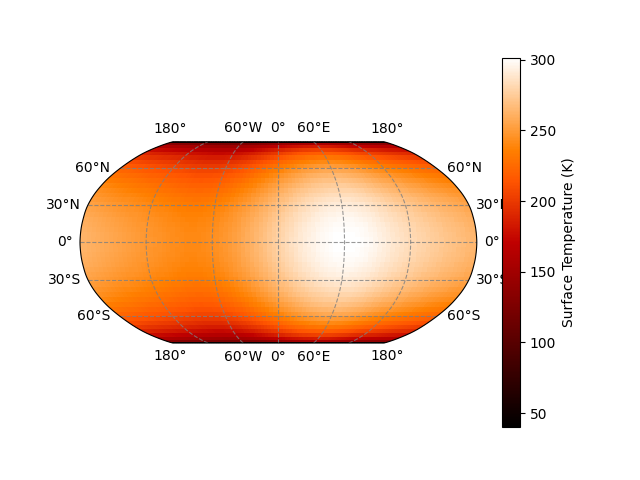
Making a surface temperature map#
Let’s make a surface map given some basic planetary parameters.
epsilon = 2*np.pi
star_teff = 5800*u.K
albedo = 0.3
r_star = 1*u.R_sun
r_orbit = 1*u.AU
tmap = ht.TemperatureMap.from_planet(
epsilon=epsilon,
star_teff=star_teff,
albedo=albedo,
r_star=r_star,
r_orbit=r_orbit
)
lons = np.linspace(-180,180,90,endpoint=False)*u.deg
lats = np.linspace(-90,90,46,endpoint=True)*u.deg
longrid,latgrid = np.meshgrid(lons,lats)
data = tmap.eval(lon=longrid,lat=latgrid,alpha=0)
fig = plt.figure()
proj = ccrs.Robinson(central_longitude=0)
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection=proj)
im = ax.pcolormesh(lons.to_value(u.deg),lats.to_value(u.deg),data.to_value(u.K),cmap='gist_heat',transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
gl = ax.gridlines(crs=ccrs.PlateCarree(),draw_labels=True,
color='grey', alpha=0.8, linestyle='--')
gl.top_xlabels = False
gl.right_ylabels = False
_=fig.colorbar(im,ax=ax,label='Surface Temperature (K)')
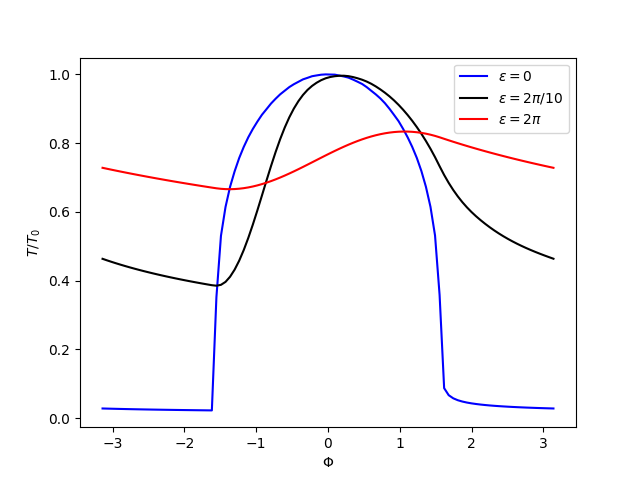
Compare different values of \(\epsilon\)#
We can recreate Figure 1 from Cowan and Agol [2011]
eps = [1e-4,0.2*np.pi,2*np.pi]
label = ['0','2\\pi/10','2\\pi']
modes = ['ivp_reflect','ivp_reflect','bvp']
colors = ['b','k','r']
n_points = 100
fig,ax = plt.subplots(1,1)
for e,l,m,c in zip(eps,label,modes,colors):
lons, tsurf = ht.get_equator_curve(e,n_points,m)
ax.plot(lons,tsurf,color=c,label=f'$\\epsilon = {l}$')
ax.set_xlabel('$\\Phi$')
ax.set_ylabel('$T/T_0$')
_=ax.legend()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.978 seconds)
